Discuss Explain Howand Whythe Results Same Different Predicted Values Mean
This helps us get an idea of. The average of the target variable in the test set is almost exactly the same as in the training set 00005.
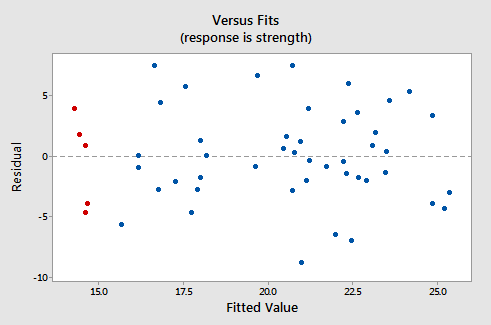
4 2 Residuals Vs Fits Plot Stat 462
Additionally differences in the version of libraries can mean the fixing of bugs and the changing of functionality that too can result in different results.

. How does the experimental result differ from the theoretical in terms of accuracy. The hours is a variable that takes the values 10 20 30 3 choices and the variable didep is a categorical variable that takes the value 1 for the alternative of the 3 choices of the hours. I performed the Prediction for new known solution to test the calibration but the result is totally unacceptable and there is a big difference between the predicted values and the actual values.
However my R2 value is typically near 0 often negative and my predicted values are all within one 10000th or less of each other so when plotted it essentially looks like a horizontal line roughly reflecting the mean value. Why the mean predicted values exphat from OLS regression indicated below is the same as the mean of the observed value. Amanda has taught high school science for over 10 years.
This is while all the variables have significant coefficients in the model. Predicted Values A predicted value or fitted value of the mean corresponding to the vector of covariates x i is given by where g is the link function regardless of whether x i corresponds to an observation or not. This is expected intuitively the variance of the population of values does not shrink when one samples from it because the random variable ε i does not decrease but the variance of the mean of the does shrink with increased sampling because the variance in and decrease so the mean response predicted response value becomes closer to.
Ive then fit it with a linear regressor and attempted to predict the values for the forthcoming 24-hour period. STUDENTi RESIDi STDERR RESIDi There are two kinds of confidence intervals for predicted values. The ratio of the residual to its standard error called the studentized residual is sometimes shown as.
The same applies to the predicted mean of the dependent variable. I run the following model. Provided that the correct model is used the theoretical probability is correct.
Using Predicted Means to Understand Our Models. The scatter plot of predicted and observed values and vice versa is still the most frequently used approach. Why OLS mean predicted values and the mean observed value ofthe dependent variable are the same.
The predicted value of the equation determines the body fat percentage according to be body mass index. This is problematic with significance testing because ones ability to detect differences is a function of sample size - the larger your sample size the more likely it is that any difference between the two values will be significant. In this example Hours studied is a continuous predictor variable that ranges from 0 to 20 hours.
Mixlogit didep hours if sex0 marital_status1. Predicted Values of the Mean. Hence it is used to calculate residuals which are the difference between the actual and the predicted values.
Additionally this also explains why you will get different results for the same algorithm on the same machine implemented by different languages such as R and Python. Predictions are precise when the observed values cluster close to the predicted values. Comparing Results of an Investigation with Predictions.
Regression predictions are for the mean of the dependent variable. Observed y-axis vs predicted x-axis OP should be used. I just havent been able to understand the code meaning of classification table vs actual.
The R squared value lies between 0 and 1 where 0 indicates that this model doesnt fit the given data and 1 indicates that the. However when I test my model on the test set the overall average of my predictions is a bit out 0001. The residual is defined as.
We get so involved in reporting statistically significant and p-values that. If the difference is zero then that data points lie on the regression line. Residual and predicted values are usually graphed and computed.
The average value of the target variable on the training set is about 00005. The standard error of the individual future predicted value yi is. If the line of best fit is the best fit then the sum of the difference between the actual value and the predicted values is always zero.
There is no consensus on which variable should be placed in each axis to present the results. If you think of any mean you know that there is variation around that mean. As discussed in the section Mean Squared Error in Chapter 3 Introduction to Statistical Modeling with SASSTAT Software both intervals are based on the mean squared error of predicting a target based on the result of the model fit.
In fact the actual estimate of the new measured value is obtained by evaluating the estimated regression function at the relevant predictor variable values exactly as is done for. When we perform linear regression on a dataset we end up with a regression equation which can be used to predict the values of a response variable given the values for the explanatory variables. Dear all i want to compare the actual with the predicted mean hours.
If the difference between the actual value and the predicted value is negative then the data points are below the regression line. The difference in the expressions for the confidence interval and the prediction interval comes about because the target of estimation is a constant. R2 remains the same for PO or OP.
Im new to R and neutral network and havent been able to figure out how predict variable from trained network neural network and produce classification table of predicted vs actual values. The mechanics of predicting a new measurement value associated with a combination of predictor variable values are similar to the steps used in the estimation of the average response value. That is the response variable can be missing and the predicted value is still computed for valid x i.
The expression cant see the forest for the trees often comes to mind when reviewing a statistical analysis. As it is depicted in the following picture there is a huge difference between actual and predicted values of my dependent variable. The predicted value helps to find the difference between the predicted value and the observed data.
We can then measure the difference between the predicted values and the actual values to come up with the residuals for each prediction. Outx is an output that shows both actual and predicted values of my model. It indicates how close the regression line ie the predicted values plotted is to the actual data values.
It is also known as the coefficient of determinationThis metric gives an indication of how good a model fits a given dataset. First it seems you would like to conclude that the predicted and actual values are not different. Now the problems are.
I would greatly appreciate it if you explain the code. For a continuous predictor variable the regression coefficient represents the difference in the predicted value of the response variable for each one-unit change in the predictor variable assuming all other predictor variables are held constant. The residuals play a vital role to validate the obtained.
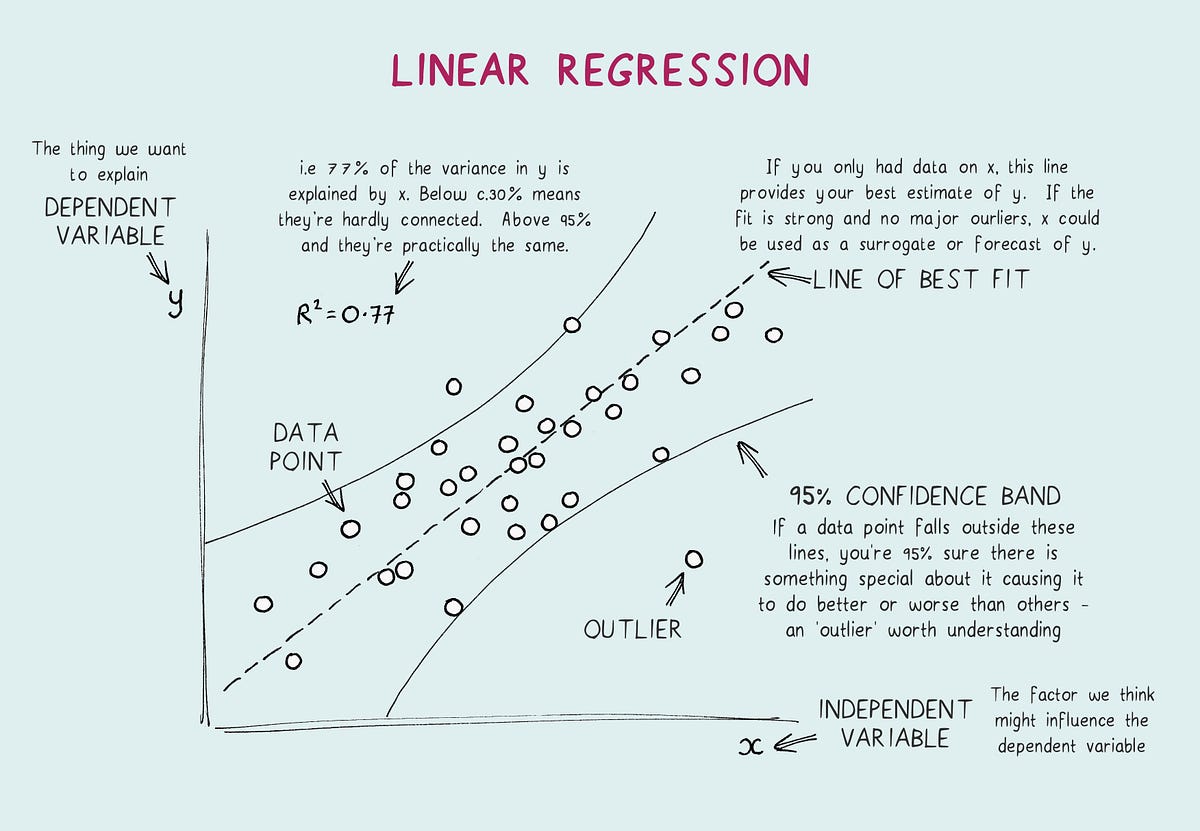
Linear Regression Explained A High Level Overview Of Linear By Jason Wong Towards Data Science
Comments
Post a Comment