Which Describes the F2 Generation in Mendel's Experiments
Gregor Mendel who is referred to as the father of genetics crossed two parents that are pure breeding for specific traits. In plants or animals that cannot self-fertilize the F2 generation is produced by crossing F1s to each other.
8 1 Mendel S Experiments Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
In the mendels experiment why did traits show up in the f2 generation that were not present in the f1 generation.
. Dominant and recessive traits Mendel described each of the trait variants as dominant or recessive Dominant traits like purple flower colour appeared in the F1 hybrids whereas recessive traits like white flower colour did not. The offspring were called the F2. Describes Mendels second set of experiments involving dihybrid crosses which demonstrated that alleles are transmitted individually.
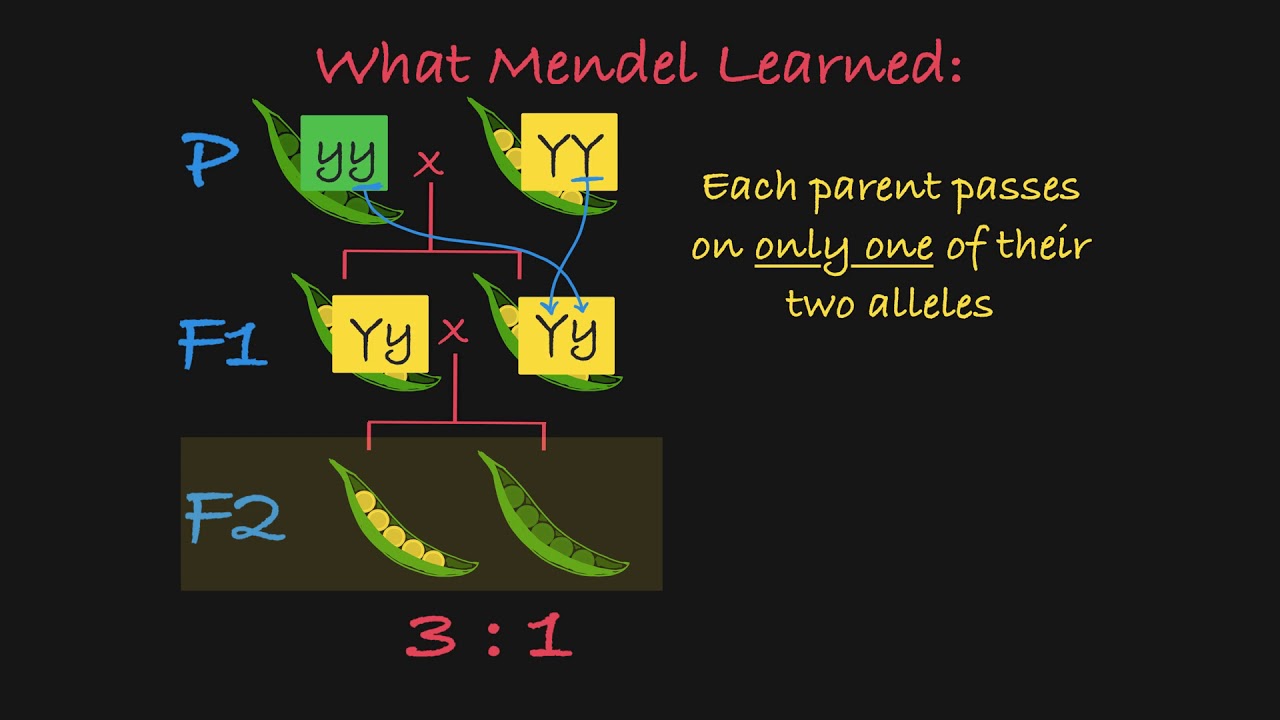
True-breeding hybridization monohybrid cross P generation F1 generation and F2 generation. New mutations were frequently generated in the cross that generated the F2 generation. AA Aa aa which yields a 31 ratio Mendel performed many experiments and consistently obtained ratios very close to.
Mendel found that in the F1 generation only round and yellow seeds are produced after crossing between round yellow and wrinkled green seeds. F2 Generation F2 generation 3 tall. He then collected and grew the seeds from the F 1 plants to produce the F 2 or second filial generation.
List the novel features of Mendels experiments and how each feature contributed to the success of his studies. In the F 1 generation half the gametes were Y and the other half were y making the F 2 generation produced from random mating 14 Yy 12 YY and 14 yy thus explaining the 31 ratio. Garden Pea Characteristics Revealed the Basics of Heredity In his 1865 publication Mendel reported the results of his crosses involving seven different characteristics each with two contrasting traits.
Mendel observed that the F2 progeny of his dihybrid cross had a 9331 ratio and produced nine plants with round yellow seeds three plants with round green seeds three plants with wrinkled. The F2 generation had three tall plants and one short plant. List and explain the four components of Mendels hypothesis that led him to deduce the law of segregation.
From the dihybrid cross Mendel got the second law of genetics. However when he allowed the hybrid plants to self-pollinate the hidden traits would reappear in the second-generation F2 hybrid plants. He allowed the F 1 plants to self-fertilize and found that 705 plants in the F 2 generation had violet flowers and 224 had white flowers.
Mendels experiments extended beyond the F 2 generation to the F 3 generation F 4 generation and so on but it was the ratio of characteristics in the P F 1 and F 2 generations that were the most intriguing and became the basis of Mendels postulates. Up to 24 cash back Stage 3 Results. Members of the F1 generation had only one allele for each trait but members of the F2 generation had two alleles for each trait.
This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. Mendel suspected that the round peas in the F2 generation consisted of both types. When he showed these seeds they grew into tall stem plants and dwarf stem plants of F2 generation giving nearly a 31 ratio of tall stem and dwarf stem plants.
Mendel allowed the plants of F1 generation to reproduce by self pollination and their seeds were obtained. 4 rows The F1 generation results from cross-pollination of two parent P plants and contained all. Importantly Mendel did not stop his experimentation there.
Mendel conducted an experiment to study the segregation and transmission of 2 pairs of contrasting traits at a time. Traits can be dominant or recessive and the recessive traits are hidden by the dominant ones in the F1 generation. But in the F2 generation 4 types of combinations were observed.
In Mendels first experiment he crossed a short plant and a tall plant. Mendel pollinated each plant from the Fl generation with its own pollen. Most people would assume the offspring would be medium-sized plants but Mendel saw something unexpected.
1 short Self-pollinated Self-pollinating the plants from the Fl generation resulted in some tall plants and some short plants. The F1 generation consists of offs. The pea plant was chosen for the experiment by Mendel because it is self-pollinating and has physical traits that are easy to distinguish and study.
The short plants reappeared in the FZ generation. The gametes from these were Y and y thereby producing an F 1 generation of Yy that were yellow in colour because of the dominance of Y. Expert Solution Want to see the full answer.
Those that are true-breeding and those that are not. The genotypic ratio F2 generation is 121242121. In Mendels breeding experiment on garden pea the offspring of F2 generation are obtained in the ratio of 25 pure yellow pod 50 hybrid green pods and 25 green pods State i which pod colour is dominant ii The Phenotypes of the individuals of F1 generation.
From these results its clear that there are two types of round peas. Mendels Second Experiment In Mendels second experiment he allowed the offspring from the first experiment to pollinate each other. The law of inheritance was proposed by Gregor Mendel after conducting experiments on pea plants for seven years.
The offspring were all tall. Iii Workout the cross. All of the F1 generation.
F2 generation. In the F 2 generation approximately three quarters of the plants had violet flowers and one quarter had white flowers. The statement that describes the F2 generation in Mendels experiments is three times as many tall plants as short plants.
The Mendels laws of inheritance include law of dominance law of segregation and law of independent assortment. Define the following terms. The ratio obtained in F2 generation was 31.
Instead Mendels results demonstrated that the white flower trait had completely disappeared in the F 1 generation. The law of segregation states that every individual possesses two alleles and only one allele is passed on to the.
3 2 Mendel S First Set Of Experiments Biology Libretexts

Comments
Post a Comment